The plastic pollution crisis is a growing concern that has captured the attention of the world. As more and more plastic waste accumulates in our oceans and waterways, the impact on our environment and the health of our planet has become increasingly clear. The statistics are staggering: 8 million tons of plastic waste enter our oceans every year, and by 2050, it is estimated that there will be more plastic in the ocean than fish. The problem is so severe that it requires immediate attention and action.
What is plastic pollution, and why is it a crisis?
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic waste in the environment, particularly in our oceans and waterways. It is caused by the improper disposal of plastic products, including single-use plastics such as water bottles, straws, and plastic bags. These products take hundreds of years to decompose, and as a result, they remain in our environment for a very long time.
The crisis we face is multifaceted. The environmental impact of plastic pollution is significant, with the potential to disrupt entire ecosystems and threaten the survival of species. In addition, plastic pollution poses a serious threat to human health. As microplastics enter the food chain, they can have negative impacts on human health. Studies have shown that microplastics can lead to inflammation, cancer, and other health problems.
The impact of plastic pollution on marine life
The impact of plastic pollution on marine life is significant and alarming. Plastic waste can entangle marine animals, causing injury or even death. In addition, marine animals can mistake plastic waste for food, leading to ingestion and blockages in their digestive systems. This can cause starvation and death.
The impact of plastic pollution is not just limited to large animals; it can also have an impact on smaller organisms. As plastic waste breaks down into smaller particles, it creates microplastics that can be ingested by tiny organisms such as plankton. These organisms are the base of the marine food chain, and the ingestion of microplastics can disrupt entire ecosystems and threaten the survival of species.
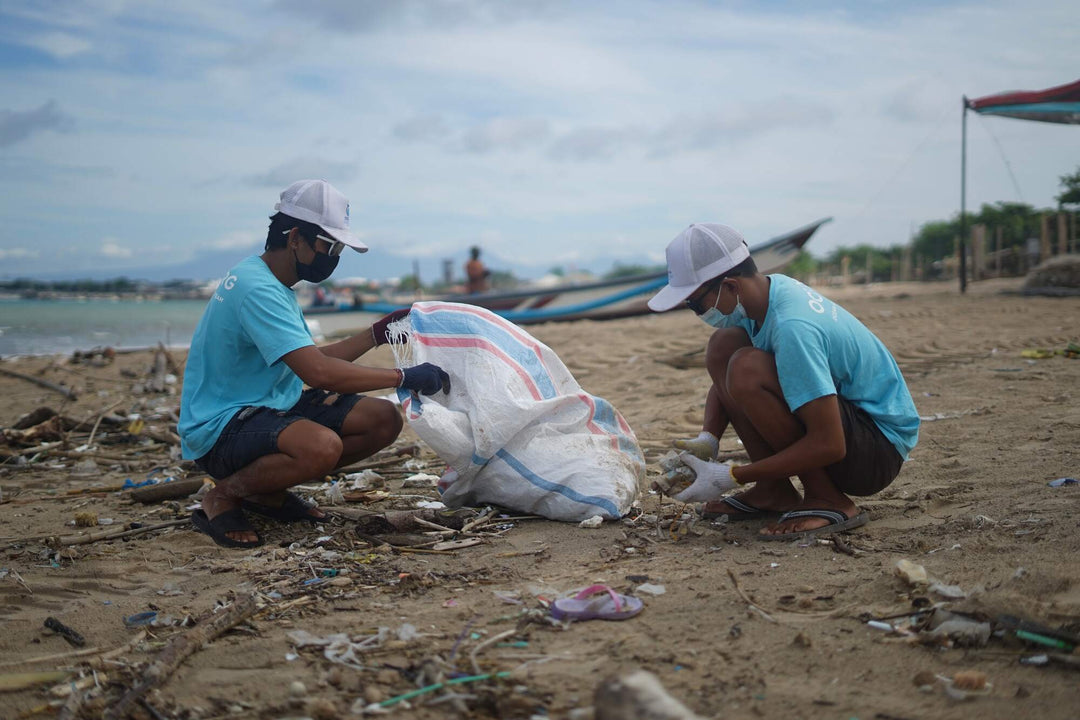

What can we do to help?
The good news is that there are many things that we can do to help reduce plastic pollution. First and foremost, we need to reduce our use of single-use plastics. This can be achieved by using reusable water bottles, shopping bags, and straws. Additionally, we should properly dispose of our plastic waste and recycle as much as possible.
Governments also have a role to play in reducing plastic pollution. They can implement policies and regulations that restrict the production and use of single-use plastics, promote recycling and waste reduction, and invest in research and development of more sustainable materials.
In addition to individual and governmental action, there are many organizations working to combat plastic pollution. These organizations work to raise awareness, educate the public, and implement solutions to reduce plastic waste.
The plastic pollution crisis is a significant environmental issue that requires immediate action. By reducing our use of single-use plastics, properly disposing of plastic waste, and advocating for government action, we can make a positive impact and help to create a more sustainable future for generations to come. It is up to each and every one of us to take action and help protect our oceans and marine life from the devastating impact of plastic pollution.